What is project schedule management? Definition, process and examples
Project schedule management is defined as the process of planning, developing, maintaining, and controlling the timelines of a project.
Project schedule management is defined as the process of planning, developing, maintaining, and controlling the timelines of a project.


Introduction
Every successful project has one thing in common: a well-planned schedule. Without it, even the most capable teams struggle with missed deadlines, shifting priorities, and constant rework. When timelines aren’t clear, progress becomes unpredictable, and decisions turn reactive. Project schedule management creates structure, visibility, and accountability, helping teams understand what needs to happen and by when, so work moves forward without unnecessary delays.
By the end of this blog, you’ll understand what project schedule management means, why it’s critical for delivering work on time, and how it helps teams stay aligned throughout a project.
What is project schedule management?
Project schedule management is defined as the process of planning, developing, maintaining, and controlling the timelines of a project. It involves identifying the specific activities that must be performed to complete the project.
Project schedule management includes estimating how long each activity will take and determining the order in which those activities should occur. The goal is to ensure that the project is completed within the agreed timeframe while efficiently using resources and managing constraints.
Schedule management includes defining activities, sequencing them logically, estimating durations, allocating resources, and creating a timeline using tools like Plane.
Techniques such as the Critical Path Method and schedule compression (e.g., crashing and fast tracking) are often used to optimize the schedule. These steps allow project managers to understand the flow of work and the dependencies that could impact timelines.
Once the schedule is established, the focus shifts to monitoring and controlling it throughout the project lifecycle. This involves regularly comparing actual progress with the planned schedule to identify variances, assess risks, and take corrective actions. Effective communication among team members and stakeholders is critical during this phase to manage expectations and resolve scheduling issues promptly.
Overall, project schedule management is essential for coordinating activities, meeting deadlines, and achieving project objectives. It supports decision-making, resource planning, and risk management, contributing to a project’s success. When done well, it enhances efficiency, reduces uncertainty, and provides a clear path from project initiation to completion.
Related: What is enterprise project management?
What project schedule management focuses on
At its core, project schedule management is about more than deadlines. It focuses on several key elements:
- Time: Estimating how long each task will take and defining start and end dates.
- Dependencies: Understanding how one task affects others and sequencing activities correctly.
- Sequence: Determining the order of tasks to avoid bottlenecks and delays.
- Delivery dates: Aligning tasks with milestones and overall project deadlines to ensure timely completion.
How it differs from simply tracking tasks
Tracking tasks shows what is happening day-to-day, but it doesn’t guide future work or help teams anticipate problems. Project schedule management, on the other hand, creates a full roadmap of the project, highlighting critical paths, potential delays, and resource allocation. It turns reactive tracking into proactive planning, helping teams stay on course even when changes occur.
Why project schedule management is important
Every project has a timeline, but without proper scheduling, even the simplest tasks can spiral into delays. Project schedule management ensures that work stays on track, resources are used wisely, and teams have visibility into progress. It helps prevent bottlenecks, reduces uncertainty, and aligns everyone toward the project’s goals.
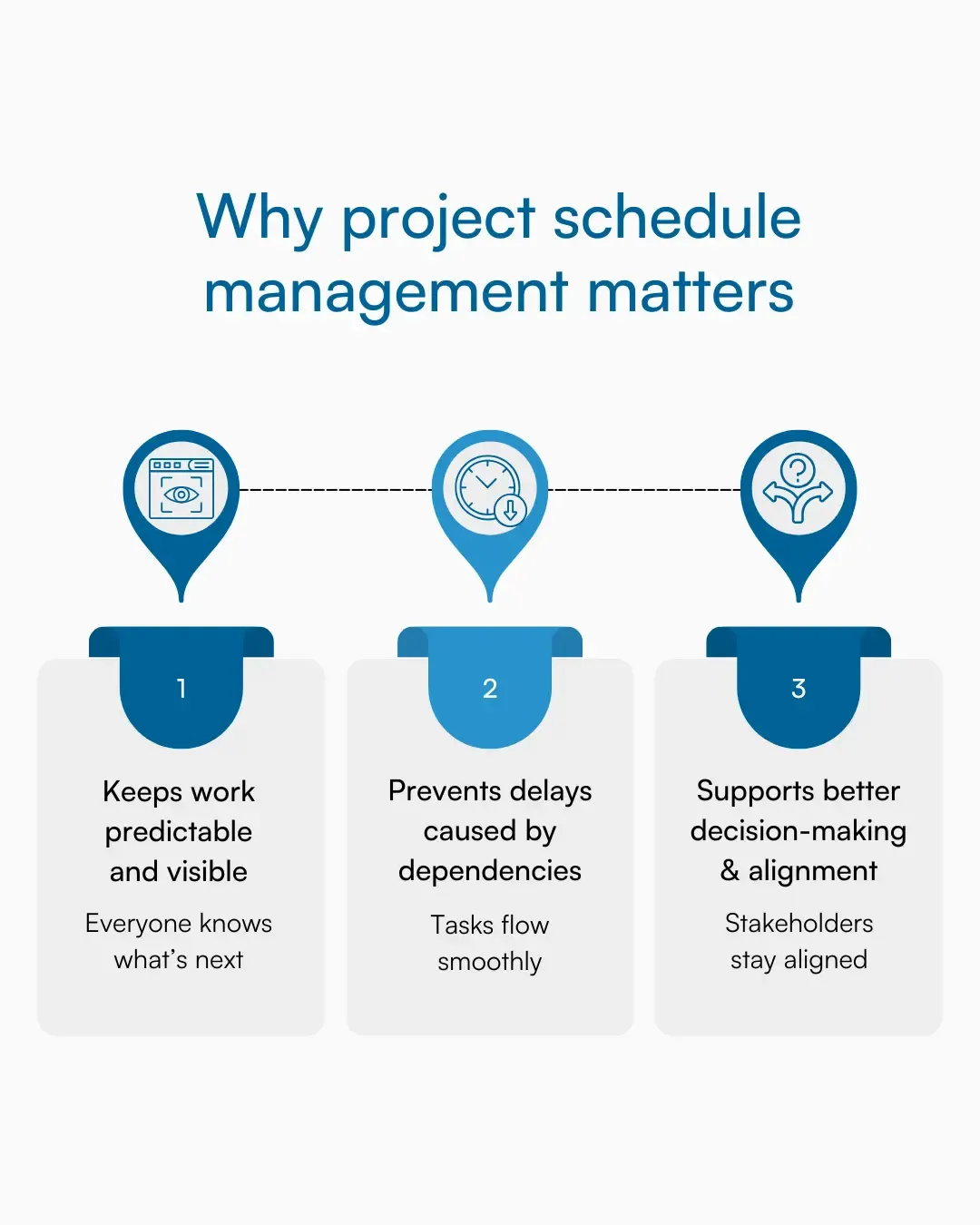
Below are the main reasons why managing your project schedule is crucial:
1. Brings predictability and visibility
A clear schedule provides a roadmap for the team. It shows what tasks need to be completed, when, and by whom, making progress measurable and predictable. With this visibility, project managers can anticipate delays and adjust plans before issues escalate.
2. Prevents delays and overload
Proper task sequencing and careful resource allocation prevent bottlenecks. Teams avoid overloading individuals and ensure critical dependencies are addressed, keeping the project flowing smoothly and on time.
3. Supports better decision-making and alignment
When timelines and dependencies are clear, stakeholders can make informed decisions. Project managers can reallocate resources, adjust deadlines, and communicate changes confidently, keeping everyone aligned and focused on delivery.
What is a schedule management plan?
A project schedule doesn’t manage itself — it needs a plan. A schedule management plan is a formal document that outlines how a project’s schedule will be developed, monitored, and controlled. It acts as a guide for the project team, helping them make consistent decisions about timelines, task sequencing, and resource allocation throughout the project lifecycle. Essentially, it sets the rules for how the schedule will be handled from start to finish.
What it is and why it exists
The schedule management plan defines the approach the team will take to plan and track project activities. It exists to ensure that everyone follows a consistent method for estimating durations, sequencing tasks, and updating timelines. Without it, schedules can become disorganized, progress hard to track, and decisions about timing inconsistent.
What it typically includes
A good schedule management plan covers several key areas:
- Standards and procedures: Guidelines for creating, formatting, and maintaining schedules.
- Tools and software: The platforms or tools (like Plane) that will be used for planning and tracking tasks.
- Update frequency: How often the schedule will be reviewed and updated, such as weekly or at milestone completion.
- Roles and responsibilities: Who is responsible for creating, maintaining, and approving schedule updates?
How it guides scheduling decisions
By clearly defining the approach and responsibilities, the schedule management plan guides all scheduling decisions. It ensures that task dependencies, durations, and resource allocations are handled consistently. When changes occur, such as delays, scope adjustments, or new tasks, the plan provides a framework for adjusting the schedule without chaos, keeping the project on track from initiation to completion.
If you’re looking for the principles behind creating effective schedules, take a look at 12 key project management principles.
Key components of the project schedule management process
Project schedule components are designed to ensure that the project is delivered on time, within scope, and with the optimal use of resources, and are as follows:
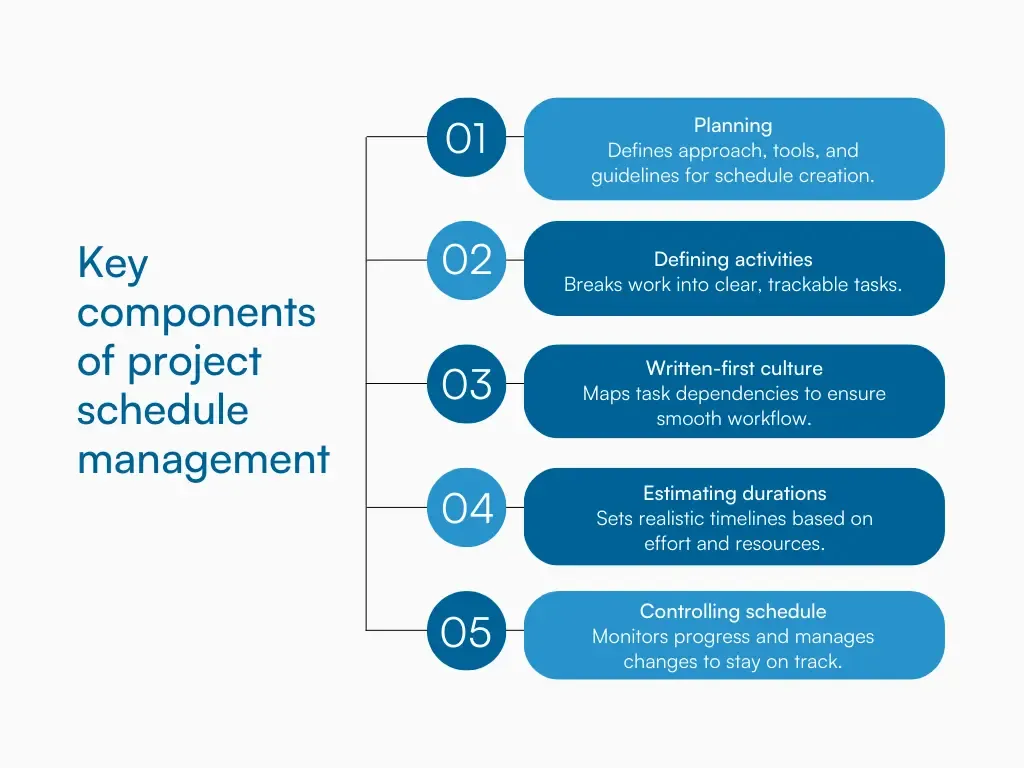
1. Planning: This is the foundational step that defines how the project schedule will be developed, managed, and controlled throughout the lifecycle of the project. It involves setting guidelines, selecting scheduling methodologies, identifying tools and resources, and establishing metrics for monitoring progress. This component acts as the roadmap for all schedule-related decisions and activities.
2. Defining activities: This involves breaking down work packages from the work breakdown structure into individual tasks or activities that need to be performed. Clearly defining activities helps in creating an accurate schedule and provides a basis for estimating time and resource requirements. Each activity should be detailed enough to be tracked and managed effectively.
3. Sequencing activities: Sequencing involves identifying relationships between tasks—such as finish-to-start or start-to-start—and creating a network diagram or flow that shows the order in which tasks must be completed. This component is crucial for identifying the critical path and understanding how delays in one activity can impact the entire schedule.
4. Estimating activity durations and developing schedule: Estimating how long each activity will take involves analyzing resources, constraints, historical data, and other factors. After durations are estimated, the schedule is developed by mapping out start and end dates, applying constraints, assigning resources, and integrating milestones. Tools like Plane help create, visualize and analyze the schedule.
5. Control schedule: This final component involves tracking progress against the planned schedule, updating it as needed, and managing changes. The project team uses performance metrics, status reports, and forecasting techniques to ensure the project stays on track and corrective actions are taken when necessary.
Related: 12 key project management principles
Common scheduling techniques used by project teams
Project teams use a variety of techniques to plan and manage schedules effectively. These methods help identify critical tasks, optimize timelines, and ensure resources are used efficiently. Understanding these techniques allows project managers to reduce delays, handle dependencies, and keep projects on track.
1. Critical Path Method (CPM)
CPM identifies the sequence of tasks that directly impacts the project’s completion date. By focusing on these critical tasks, teams can prioritize work, anticipate delays, and understand which activities require the most attention to maintain the schedule.
2. Schedule buffers and slack
Buffers and slack provide flexibility in the timeline. Buffers are extra time added to critical tasks or phases to account for uncertainty. At the same time, slack is the amount of time a non-critical task can be delayed without affecting the overall project. Both help absorb minor delays without impacting the final delivery date.
3. Fast tracking and crashing
Fast tracking involves performing tasks in parallel that would typically happen sequentially to shorten the schedule. Crashing adds additional resources to critical tasks, allowing them to be completed faster. These techniques help compress timelines when deadlines are tight, while carefully managing risks and costs.
4. Resource leveling
Resource leveling balances workloads by adjusting task schedules based on resource availability. It ensures that team members and equipment are not over-allocated, helping maintain efficiency and prevent burnout while keeping the project on track.
Examples of project schedule management
Here are examples of project schedule management across different industries, showing how the process is tailored to fit each industry's unique characteristics, workflows, and deliverables:
1. Software development
In software projects, schedule management involves planning and tracking tasks such as coding, testing, and deployment within tight deadlines and often using iterative approaches.
Example: A team building a mobile app follows a two-week sprint cycle. The project schedule includes defining tasks such as UI/UX design, backend development, API integration, testing, and deployment. Dependencies are mapped (e.g., development must precede testing), and tools like Plane are used to track task progress. The critical path may include activities like “develop user login,” which must be completed before any authentication testing begins.
2. Marketing campaign
Marketing projects typically involve coordination among creative, communication, and digital teams with fixed launch dates.
Example: A marketing team plans a product launch campaign with a deadline two months away. Key scheduled activities include concept creation, content development, media buying, campaign testing, and go-live. Activities are sequenced to allow approval and revisions. Tools like Plane help visualize these tasks. If content development takes longer than expected, the team uses fast-tracking by starting media placement before final approvals are complete.
3. Event management
Event planning relies on scheduling to align logistics, vendors, venues, and promotional activities with the event date.
Example: A conference planning team creates a schedule that includes venue booking, speaker confirmation, attendee registration, marketing, logistics, and post-event reporting. Dependencies include finalizing speakers before publishing agendas. Delays in speaker confirmation may require adjusting the promotion schedule. Ideally, project management platforms like Plane should be used to monitor task completion.
4. Product development (manufacturing)
Manufacturing product development schedules must align with prototyping, testing, regulatory approvals, and mass production.
Example: A company designing a new consumer appliance schedules activities like market research, design modelling, prototype testing, quality control, and production setup. Each phase is dependent on the successful testing of the previous one. Delays in prototype testing could affect time-to-market, prompting the use of concurrent engineering (parallel task execution) to compress the schedule.
5. Construction
Construction projects require precise scheduling of labor, materials, equipment, and subcontractors to avoid costly delays.
Example: A residential building project uses schedule management to coordinate tasks like site preparation, foundation work, framing, electrical, plumbing, and finishing. A network diagram shows dependencies such as "foundation must be completed before framing starts." If weather delays foundation work, the team might crash the schedule by adding extra workers to the framing task.
Related: What is project cycle management?
Common challenges in project schedule management
Even with a solid plan, projects can face challenges that affect timelines and delivery. Understanding these common obstacles helps teams prepare, mitigate risks, and maintain control over the schedule.
1. Unrealistic timelines
Setting deadlines that are too tight or based on assumptions rather than data can create pressure and lead to missed targets. Realistic timelines are built using accurate estimates, historical data, and team input.
2. Ignored dependencies
Overlooking task dependencies can cause delays, as one task may rely on the completion of another. Mapping dependencies clearly ensures that work flows in the correct order and critical paths are respected.
3. Resource overallocation
Assigning too many tasks to the same team members or overusing equipment can slow progress and create bottlenecks. Resource planning and leveling help balance workloads and maintain steady progress.
4. Frequent scope changes
Changes in project requirements or priorities can disrupt the schedule if they are not managed carefully. Incorporating change management processes and flexible scheduling techniques helps absorb adjustments without derailing the timeline.
5. Poor schedule updates
Failing to update the schedule regularly reduces visibility and increases the risk of surprises. Consistent monitoring, tracking progress, and updating timelines ensure the project stays aligned with goals and deadlines.
Best practices for project schedule management
Effective project schedule management relies on a set of best practices that help ensure timely delivery, efficient resource use, and minimal disruptions. These practices apply across industries and can significantly improve the quality, reliability, and flexibility of the project timeline. Below are some widely recognized best practices for project schedule management:
1. Define clear and complete activities:
Ensure that each activity is well-defined, has clear boundaries, and is measurable. This level of detail supports accurate time estimates and easier tracking.
Avoid vague task names like "do testing"—instead use "conduct user acceptance testing for module A."
2. Use logical sequencing and identify dependencies:
Sequence activities based on their real-world dependencies, using tools such as network diagrams or dependency matrices. Regularly review dependencies to identify opportunities to fast-track or overlap tasks where feasible.
3. Apply realistic time and resource estimates:
Use historical data, expert judgment, and estimation techniques (such as three-point estimates) to develop accurate duration estimates. Also consider resource availability and limitations to avoid over-allocation or unrealistic timelines.
Involve team members in estimation to improve accuracy and commitment.
4. Use appropriate scheduling tools:
Select scheduling software that matches the scale and complexity of the project. Tools like Plane provide visualizations such as Gantt charts and burndown charts that help manage and communicate the schedule effectively.
Keep the schedule dynamic and regularly updated rather than treating it as a one-time plan.
5. Monitor and control the schedule proactively:
Track progress against the baseline regularly and use metrics like schedule variance or earned value to assess performance. Adjust the schedule promptly in response to delays or changes, and communicate updates to all stakeholders.
Set regular review intervals (e.g., weekly updates) and use forecasts to predict future issues before they arise.
6. Include buffers and contingency planning
Build flexibility into the schedule by including time buffers for high-risk activities or phases with uncertainty. This helps absorb minor delays without affecting the overall timeline.
Use management reserve time wisely and document when and why it's used.
7. Communicate clearly with all stakeholders
Ensure all team members and stakeholders understand the schedule, their responsibilities, deadlines, and the impact of delays. Transparent communication builds trust and keeps the team aligned.
Share schedule milestones and critical path insights in reports and status meetings.
How project schedule management fits into project management
Project schedule management is a key part of overall project management. It connects timelines with scope, resources, and costs, ensuring that all aspects of a project work together smoothly. Understanding its place in the bigger picture helps teams make informed decisions and achieve project objectives efficiently.
1. Relationship with scope, cost, and resources
Schedules are closely linked to the project scope, budget, and available resources. Changes in one area affect the others. For example, adding tasks increases resource needs and may extend timelines. Integrating these elements ensures that the project remains balanced and achievable.
2. Difference between a project plan and a project schedule
A project plan provides a high-level overview of objectives, deliverables, and processes. The project schedule, on the other hand, focuses on the timing of tasks and milestones. While the plan outlines what needs to be done, the schedule defines when it will happen and who will do it.
3. Why scheduling cannot work in isolation
Scheduling is most effective when combined with other project management activities such as risk management, communication, and resource planning. A well-managed schedule ensures that decisions are informed by real constraints and dependencies, keeping the project aligned with its goals.
Final thoughts
Project schedule management is essential for keeping work organized, predictable, and aligned with project goals. Effective scheduling helps teams meet deadlines, optimize resources, and respond to changes without losing momentum. By creating schedules that are practical, flexible, and clearly communicated, project managers can guide their teams toward successful, on-time project delivery while maintaining clarity and control throughout the project lifecycle.
Frequently asked questions
Q1. What are the key processes within project schedule management?
Project schedule management involves six key processes:
- Planning the schedule approach: Defining how the schedule will be created, tracked, and controlled.
- Defining activities: Breaking down work into manageable, trackable tasks.
- Sequencing activities and dependencies: Identifying task relationships to understand the order of execution.
- Estimating activity durations: Calculating how long each task will take based on resources and constraints.
- Developing the project schedule: Turning tasks and estimates into a timeline with milestones.
- Monitoring and controlling the schedule: Tracking progress, managing changes, and addressing risks and delays.
Q2. What are some techniques for optimizing a project schedule?
Teams use several techniques to optimize schedules, including:
- Critical Path Method (CPM): Identifies the most extended sequence of dependent tasks to prioritize critical activities.
- PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique): Uses probability estimates to account for uncertainty in task durations.
- Schedule buffers and slack to allow for flexibility in the event of delays.
- Fast tracking and crashing: Accelerates timelines by overlapping tasks or adding resources.
- Resource leveling: Balances workload to prevent over-allocation of resources.
Q3. Compare the Critical Path Method and PERT for project scheduling
- Critical Path Method (CPM) focuses on identifying the sequence of tasks that directly impact the project’s finish date. It is deterministic and works well for projects with well-defined activities.
- PERT accounts for uncertainty by using optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely duration estimates for tasks. It is probabilistic and ideal for projects where task durations are less predictable.
Q4. What challenges can arise during project schedule development and management
Common challenges include:
- Setting unrealistic timelines
- Ignoring dependencies between tasks
- Resource overallocation
- Frequent scope changes
- Poor schedule updates and tracking
Q5. What is the difference between a project plan and a project schedule?
A project plan outlines objectives, deliverables, and overall processes. A project schedule focuses specifically on the timing of tasks, milestones, and deadlines. The schedule brings the plan to life by specifying when work happens and who is responsible.
Recommended for you