Introduction
A release planning meeting runs smoothly, tasks move across boards, and updates flow through multiple channels, yet delivery timelines still shift and decisions take longer than expected. Collaboration fills every workday, but its impact on team effectiveness often remains unclear. This guide explores the collaboration metrics that reveal how work actually moves across teams, how alignment influences execution, and how to measure team effectiveness using practical, outcome-focused signals. You will learn which metrics matter, how to track them without adding overhead, and how modern teams use collaboration data to improve delivery, clarity, and performance.
What are collaboration metrics?
Collaboration metrics show how work flows between individuals and teams during planning, execution, and delivery. They capture signals such as decision speed, clarity of ownership, knowledge sharing, and the smoothness of handoffs across functions.

When these signals remain strong, teams maintain alignment and deliver work predictably. When they weaken, delays, rework, and confusion begin to appear.
In simple terms, collaboration metrics answer three core questions:
- How smoothly does work move across teams?
- How clearly do people communicate and make decisions?
- How effectively does coordination translate into outcomes?
By tracking these signals, teams gain a structured way to measure collaboration within projects and improve how work gets done.
How collaboration metrics show how work moves across teams
Every project involves multiple contributors, from planning and design through development, review, and delivery. Collaboration metrics make this movement visible by tracking:
- How many handoffs occur across teams
- How long do decisions take
- How often does rework happen due to misalignment
- How quickly teams resolve dependencies
These metrics reveal whether coordination strengthens delivery or creates friction. Instead of relying on perception, teams gain clear insight into how collaboration influences speed, quality, and alignment across functions.
How collaboration metrics connect communication, coordination, and delivery
Strong collaboration is reflected in three areas: communication quality, coordination across teams, and delivery outcomes. Collaboration metrics connect these areas by showing how conversations and decisions translate into execution. For example, faster decision cycles often lead to shorter delivery timelines, while clearer documentation reduces repeated discussions and rework.
Tracking collaboration metrics for teams helps leaders and project managers understand whether communication supports delivery goals, whether ownership remains clear, and whether teams maintain alignment as work progresses.
Collaboration metrics vs. productivity metrics
Productivity metrics measure output, such as tasks completed, hours worked, or features delivered. Collaboration metrics measure how effectively teams work together to produce that output. A team may deliver high output despite constant coordination friction, repeated clarifications, and delays in dependencies. Collaboration metrics highlight these underlying issues by focusing on alignment, communication quality, and workflow efficiency rather than output alone.
Collaboration metrics vs. performance metrics
Performance metrics evaluate individual or team results against goals, such as revenue targets, delivery timelines, or quality benchmarks. Collaboration metrics evaluate the quality of coordination that enables those results. They provide context behind performance by showing whether strong alignment, clear decisions, and shared ownership support outcomes across teams.
Together, performance metrics and collaboration metrics provide a complete view of how results are achieved.
Why measuring collaboration matters for modern teams
Modern teams rely on constant coordination across functions, tools, and time zones. Work rarely moves in a straight line from planning to delivery. It passes through multiple contributors, reviews, and decisions, which makes collaboration a central factor in team effectiveness. Measuring collaboration helps teams understand how this coordination shapes outcomes and where improvements can strengthen execution.
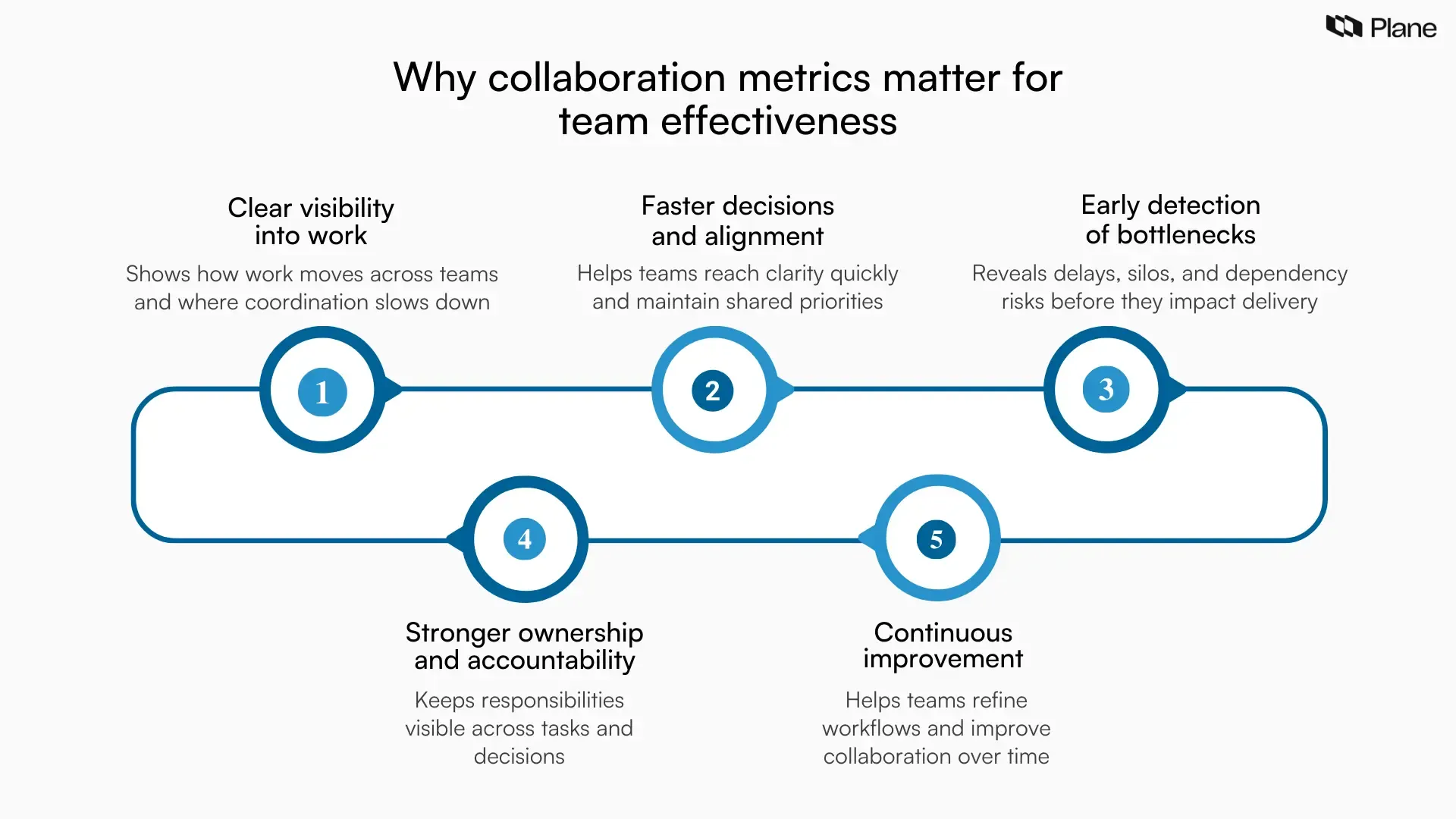
1. Better visibility into how work actually gets done
Most teams track timelines, deliverables, and output, yet the path work takes between those milestones often remains unclear. Collaboration metrics provide visibility into how tasks move across teams, where delays occur, and how decisions influence progress. This visibility helps project managers and engineering leaders determine whether execution is flowing smoothly or slowing due to unclear ownership, repeated clarifications, or dependency issues. Clear insight into workflow patterns allows teams to make informed adjustments and maintain delivery momentum.
2. Faster decision-making and stronger alignment
Decision speed plays a major role in team effectiveness. When teams measure collaboration, they gain insight into how quickly decisions move from discussion to action and how consistently priorities remain aligned across functions. Tracking metrics such as decision turnaround time, goal alignment, and clarity of next steps helps teams identify where communication strengthens execution and where it delays it. Faster and clearer decisions lead to more predictable delivery and stronger coordination across teams.
3. Early detection of bottlenecks and silos
Bottlenecks often emerge gradually through repeated delays, unresolved dependencies, or fragmented information across teams. Collaboration metrics help detect these patterns early by highlighting where work slows down, where communication gaps appear, and where teams operate in isolation. Early detection allows teams to resolve structural issues before they impact delivery timelines or product quality. Measuring collaboration across functions also reveals whether silos are forming and where cross-team coordination needs improvement.
4. Improved accountability and ownership
Clear ownership supports effective collaboration. When responsibilities remain visible and decisions are tied to accountable owners, teams execute with greater clarity. Collaboration metrics such as task ownership consistency, decision follow-through, and dependency resolution rates help teams maintain accountability across projects. Measuring these signals ensures that responsibilities remain defined and that work progresses without confusion about ownership or next steps.
5. Continuous improvement and team learning
Teams that measure collaboration regularly gain a stronger foundation for improvement. Metrics reveal patterns across sprints, releases, and projects, helping teams understand what strengthens coordination and what introduces friction. Regular reviews of collaboration data encourage teams to refine workflows, improve communication practices, and strengthen knowledge sharing. Over time, these insights support continuous improvement and build stronger team learning loops.
6. What gets measured gets improved
When teams measure collaboration intentionally, they shift from assumptions to evidence. Clear metrics highlight how coordination influences outcomes and where adjustments create meaningful impact. Measuring collaboration metrics for teams provides the visibility needed to improve alignment, strengthen execution, and maintain consistent delivery across complex projects.
Quantity vs. quality: The collaboration trap most teams fall into
Many teams mistake frequent communication for strong collaboration. Constant meetings, active channels, and continuous updates create a sense of alignment but rarely improve speed or clarity. Effective collaboration focuses on quality over quantity. Here, we explore how excessive collaboration hinders execution and define what true collaboration looks like in high-performing teams.
Why does more communication not always improve collaboration
An increase in meetings, messages, and status updates often signals coordination effort rather than coordination effectiveness. Teams may spend significant time discussing work without improving decision speed or execution clarity. When communication lacks structure or purpose, it adds noise instead of insight. Collaboration metrics help teams evaluate whether conversations lead to clear decisions, defined ownership, and measurable progress. Tracking outcomes instead of activity ensures that collaboration supports delivery rather than overwhelming it.
How over-collaboration slows execution
Excessive coordination introduces delays through repeated reviews, extended feedback cycles, and unclear decision authority. Work moves across multiple stakeholders without clear next steps, creating friction across project timelines. Teams that measure collaboration in project teams often find that too many touchpoints increase rework and delays in dependencies. Monitoring metrics such as decision turnaround time, handoff frequency, and dependency resolution speed helps teams identify when collaboration begins to slow execution rather than support it.
Effective collaboration centers on clarity and outcomes
Effective collaboration aligns communication with delivery goals. It ensures that discussions produce decisions, that decisions translate into action, and that action drives measurable outcomes. Collaboration metrics for teams highlight whether coordination strengthens alignment and execution. When teams track clarity of ownership, speed of decision-making, and quality of knowledge sharing, they gain a clearer view of how collaboration influences performance across projects.
What good collaboration looks like in practice
Strong collaboration shows up through consistent patterns across teams and projects. These patterns make it easier to measure team effectiveness and improve coordination.
- Clear ownership: Every task and decision connects to a responsible owner. Teams move forward with confidence when accountability remains visible and consistent.
- Fewer unnecessary handoffs: Work flows smoothly across functions with minimal back-and-forth. Reduced handoffs lower the risk of delays and repeated clarifications.
- Faster decisions: Teams move from discussion to decision quickly. Clear decision authority and structured communication improve execution speed and alignment.
- Shared context and documentation: Information remains accessible across teams. Well-maintained documentation and visible updates reduce confusion and support consistent collaboration across projects.
When teams focus on these signals, collaboration shifts from constant activity to purposeful coordination that strengthens delivery and team effectiveness.
A simple framework for measuring collaboration effectively
Measuring collaboration is valuable when it aligns with how teams plan, execute, and deliver work. A structured framework enables teams to track collaboration metrics effectively, fostering clear, repeatable systems that enhance delivery and alignment across projects.
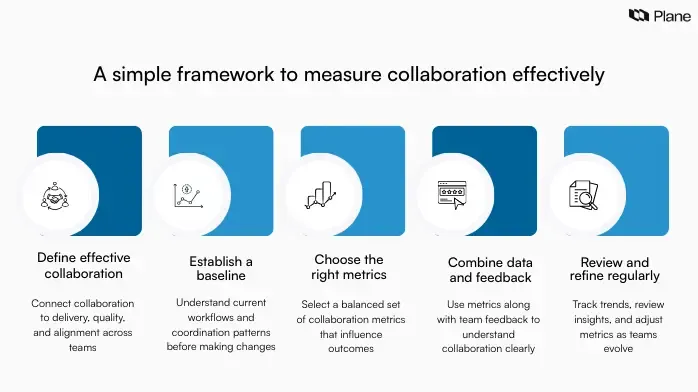
1. Define what effective collaboration means for your team
Effective collaboration varies across teams depending on goals, workflows, and delivery models. Product, engineering, and cross-functional teams need a shared understanding of what strong collaboration looks like in their context.
Start by linking collaboration to measurable outcomes, such as delivery predictability, output quality, and cross-functional alignment. Identify behaviors that support these outcomes, including clear ownership, timely decisions, and consistent knowledge sharing. When teams define collaboration through outcomes and observable behaviors, collaboration metrics become easier to track and interpret.
2. Establish a baseline before making changes
Teams often introduce new metrics or processes without understanding their current state. Establishing a baseline helps teams accurately and contextually measure collaboration within project teams.
Review recent projects and workflows to understand current decision timelines, handoff frequency, dependency delays, and communication patterns. This baseline provides a reference point for evaluating improvement. Setting targets without baseline data can lead to unrealistic expectations and misleading conclusions.
3. Choose a balanced set of metrics
A small, focused set of collaboration metrics provides clearer insights than a long list of disconnected signals. Select a mix of leading indicators, such as decision turnaround time or dependency resolution speed, and lagging indicators, such as delivery predictability or rework rates.
Avoid tracking excessive metrics that create noise and dilute focus. Prioritize signals that influence outcomes and reflect how work moves across teams. Balanced collaboration KPIs help teams understand both current performance and future risk areas.
4. Combine quantitative and qualitative insights
Numbers provide structure, while feedback provides context. Effective measurement of team collaboration requires combining both. Quantitative metrics highlight patterns in execution, while qualitative inputs from retrospectives, feedback sessions, and stakeholder reviews explain why those patterns exist.
For example, a longer decision cycle may reflect unclear ownership or fragmented documentation. Pairing metrics with team feedback helps leaders interpret collaboration data accurately and take meaningful action.
5. Review and refine metrics regularly
Collaboration evolves as teams scale, priorities shift, and workflows change. Metrics should evolve alongside them. Establish a consistent review cadence to keep collaboration metrics relevant and actionable.
Monthly reviews help teams identify short-term patterns and address immediate issues. Quarterly reviews provide space to reassess which metrics still reflect team effectiveness and which require adjustment. Regular refinement ensures that collaboration metrics continue to support alignment, execution, and continuous improvement across teams.
Key collaboration metrics that indicate team effectiveness
There is no single metric that defines collaboration. Team effectiveness becomes visible when teams track a focused set of signals that show how work moves, how decisions happen, and how alignment translates into outcomes. The following collaboration metrics provide a practical way to measure team effectiveness across projects and functions.
1. Cycle time
Cycle time measures how long work takes from execution start to completion. It reflects how smoothly tasks move from active work to completion. Short, stable cycle times indicate clear ownership, strong coordination, and minimal friction among contributors. Longer or inconsistent cycle times often indicate unclear requirements, repeated clarifications, or delays in dependencies. Tracking cycle time across projects helps teams understand whether collaboration supports steady execution or introduces bottlenecks.
2. Lead time
Lead time measures the total time from request to completion. It captures the full journey of work, from planning and prioritization through execution to delivery. When collaboration remains strong across teams, lead time stays predictable and consistent. Longer lead times often point to delays in alignment, approval cycles, or cross-team coordination. Measuring lead time helps teams evaluate how collaboration influences delivery speed and planning accuracy.
3. Time to decision
Time to decision measures how quickly teams move from discussion to a clear direction. Projects often slow down when decisions remain unresolved or require multiple review cycles. Faster decision timelines reflect strong alignment, defined ownership, and structured communication. Slower decisions often indicate fragmented context or unclear authority. Tracking this metric helps teams understand how collaboration affects execution momentum and delivery timelines.
4. Dependency resolution time
Most projects rely on multiple teams working together. Dependency resolution time measures how quickly teams address blockers that require input or action from other teams. Faster resolution signals strong coordination and shared priorities across functions. Slower resolution often reveals communication gaps or unclear ownership. Monitoring this metric helps teams strengthen cross-team collaboration and reduce delivery delays.
5. Rework rate
Rework rate tracks how often completed work requires revisions due to misalignment or incomplete information. Frequent revisions usually indicate gaps in communication, unclear requirements, or limited shared context. Lower rework rates reflect strong collaboration during planning and execution. Measuring rework helps teams determine whether collaboration clarifies the workflow early on or introduces repeated corrections later.
6. Project completion predictability
Project completion predictability measures how consistently teams deliver work on time. High predictability indicates realistic planning, strong coordination, and effective communication across teams. Low predictability often results from shifting priorities, unresolved dependencies, or unclear ownership. This metric directly links collaboration quality to delivery reliability and team effectiveness.
7. Response time for critical work
Response time measures how quickly teams address important updates, feedback requests, or blockers. Timely responses maintain execution flow and reduce delays across projects. Slower response patterns can signal overload, unclear priorities, or fragmented communication channels. Tracking response time helps teams maintain coordination and ensure that collaboration supports delivery speed.
8. Meeting effectiveness rate
Meeting effectiveness is assessed by whether discussions lead to clear outcomes, such as decisions, next steps, or assigned owners. High meeting frequency without clear outcomes often slows execution. Effective meetings produce actionable decisions and maintain alignment across teams. Measuring effectiveness through decision tracking or follow-up completion helps teams ensure that collaboration drives progress rather than prolonged discussion.
9. Documentation and knowledge sharing rate
This metric measures how consistently teams document decisions, processes, and project context. Strong documentation reduces repeated questions, improves onboarding, and supports cross-team visibility. Low documentation levels often create information silos and repeated clarification loops. Tracking contributions, updates, and usage of shared knowledge helps teams maintain alignment and improve collaboration across projects.
10. Team sentiment and engagement trend
Team sentiment reflects how individuals experience collaboration within their workflows. Regular feedback through short surveys or retrospectives helps teams identify friction, overload, or alignment gaps. Positive engagement trends often correlate with strong coordination and clear ownership. Monitoring sentiment helps leaders maintain sustainable collaboration practices and strengthen long-term team effectiveness.
Tracking these collaboration metrics for teams provides a clear view of how coordination influences execution, alignment, and outcomes. When teams measure these signals consistently, they gain the insight needed to improve collaboration and deliver work more effectively.
How to collect collaboration data without creating friction
Collaboration metrics become valuable only when teams can collect data consistently without disrupting daily work. The goal is to build visibility into how teams collaborate while maintaining trust and keeping processes simple. A structured approach helps teams measure collaboration in a way that supports execution rather than adding overhead.
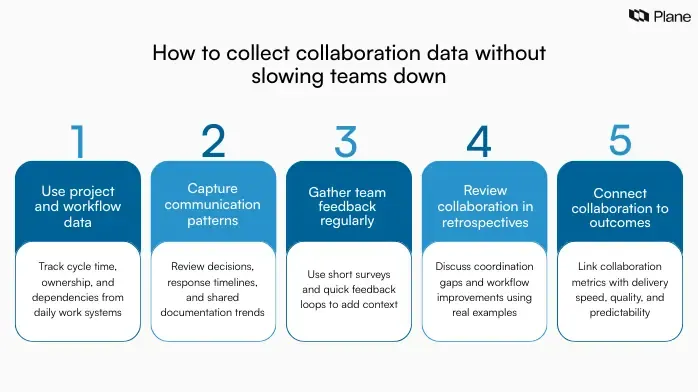
1. Use project and work management tools as the primary data source
Project and work management systems already capture how work moves across teams. They provide reliable data on cycle time, completion rates, ownership, dependencies, and decision timelines. Instead of creating separate tracking systems, teams can use existing workflows to measure collaboration metrics.
Review work items, status changes, handoffs, and blockers to understand how coordination affects delivery. This approach keeps data collection aligned with daily execution and avoids extra reporting effort.
2. Capture signals from communication and documentation systems
Communication channels and shared documentation reveal how teams exchange context and make decisions. Messages, comments, meeting notes, and shared documents show how information flows across projects. Track patterns such as response times for critical discussions, documentation clarity, and decision follow-through. Focus on high-level trends rather than individual activity to maintain trust and ensure that collaboration metrics support improvement rather than surveillance.
3. Use short surveys and feedback loops for qualitative insights
Quantitative metrics show what is happening, while feedback explains why. Short pulse surveys and feedback loops help teams understand how collaboration feels across functions. Ask focused questions about clarity of goals, ease of coordination, and access to information. Keep surveys brief and consistent to encourage participation. These insights provide context for interpreting collaboration KPIs and identifying areas for improvement.
4. Review collaboration patterns during retrospectives and project reviews
Retrospectives and project reviews offer structured opportunities to analyze collaboration data. Teams can discuss dependency delays, decision bottlenecks, and communication gaps using real project examples. Document insights and recurring patterns during these sessions. Over time, these records help teams identify trends and refine collaboration practices across projects.
5. Connect collaboration data to performance and delivery outcomes
Collaboration metrics gain meaning when linked to delivery outcomes such as completion rates, predictability, and quality. Compare collaboration signals with project performance data to understand how coordination influences results.
For example, improved decision timelines may align with faster delivery cycles, while clearer documentation may reduce rework. Connecting collaboration data to outcomes helps teams focus on metrics that drive meaningful improvements.
6. Maintain a balance between visibility and trust
Effective measurement requires transparency without creating a sense of monitoring. Focus on team-level trends rather than individual activity. Communicate clearly about why collaboration metrics are being tracked and how insights will support improvement.
When teams trust the purpose behind measurement, they engage more openly with feedback and improvement efforts. This balance ensures that collaboration metrics strengthen alignment and performance while maintaining a healthy team culture.
How to interpret collaboration metrics correctly
Collecting collaboration metrics is only the first step. Real value comes from interpreting those metrics in a way that strengthens team effectiveness and supports better decisions. Without clear interpretation, teams risk drawing incorrect conclusions or focusing on the wrong improvements. Let's look at the following approach to interpret collaboration metrics in a way that drives meaningful action and sustained improvement:
1. Focus on trends instead of isolated numbers
A single data point rarely reflects the true state of team collaboration. Short-term fluctuations can occur due to release cycles, workload changes, or shifting priorities. Looking at trends across multiple weeks or sprints provides a more accurate view of how collaboration evolves.
Consistent patterns in cycle time, decision speed, or dependency resolution reveal whether coordination is improving or creating friction. Trend-based analysis helps teams identify structural issues and measure the impact of process changes over time.
2. Compare metrics against a clear baseline
Metrics gain meaning only when compared with a starting point. A baseline shows how teams collaborated before introducing new workflows, tools, or practices. Without this reference, it becomes difficult to determine whether changes improve team effectiveness.
Compare current performance with historical data to evaluate progress. This comparison helps teams understand whether improvements in collaboration metrics lead to more predictable delivery and stronger alignment across projects.
3. Combine multiple metrics for a complete view
No single metric can fully capture collaboration quality. Teams gain a clearer picture by analyzing related metrics together. For example, faster cycle times combined with higher rework rates may indicate rushed decisions or unclear requirements. Faster decisions paired with stable delivery timelines often signal stronger alignment.
Combining collaboration KPIs provides context and prevents misinterpretation. It ensures that improvements in one area do not create unintended issues in another.
4. Use insights to improve workflows rather than monitor activity
Collaboration metrics should support improvement, learning, and alignment across teams. Their purpose is to reveal friction points and guide better ways of working. When teams use metrics to refine workflows, clarify ownership, and strengthen communication, collaboration improves naturally.
Maintaining this focus builds trust and encourages teams to engage openly with measurement efforts. Collaboration metrics for teams should always support better execution and shared outcomes.
5. Connect metrics to outcomes and decisions
Collaboration metrics become meaningful when linked to delivery outcomes and decision quality. Improvements in decision speed, documentation clarity, or dependency resolution should align with better delivery predictability and stronger alignment across teams.
Use collaboration data to guide planning decisions, workflow adjustments, and process improvements. When metrics directly inform decisions, they become a practical tool for strengthening team effectiveness and improving how work gets done.
Common mistakes teams make when measuring collaboration
Collaboration metrics help teams improve alignment and execution when used thoughtfully. Poor measurement practices can create confusion, reduce trust, and shift focus away from meaningful outcomes.

The following mistakes appear frequently when teams attempt to measure collaboration. Each one has a simple corrective approach that keeps measurement practical and useful:
1. Tracking too many metrics
Teams often try to measure every aspect of collaboration at once. A long list of metrics creates noise and makes it difficult to identify what actually influences delivery. Excessive tracking also increases reporting effort without improving insight.
Focus on a small set of collaboration metrics that directly reflect team effectiveness, alignment, and execution flow. A focused set of signals helps teams identify patterns quickly and take meaningful action without unnecessary complexity.
2. Measuring tool activity instead of outcomes
Activity within tools can appear as collaboration, yet high activity does not always lead to better results. Counting messages, comments, or meetings without linking them to outcomes can lead to misleading conclusions.
Measure how collaboration influences delivery timelines, decision speed, rework rates, and alignment across teams. Outcome-focused metrics provide a clearer view of how coordination supports project success and team effectiveness.
3. Ignoring qualitative context
Metrics provide structure, while context explains why patterns exist. Relying only on numbers can lead to incomplete interpretations. For example, slower cycle times may reflect complex project requirements rather than coordination issues.
Combine collaboration metrics with feedback from retrospectives, surveys, and project reviews. This context helps teams understand the reasons behind trends and identify the most effective improvements.
4. Using metrics for micromanagement
Collaboration metrics lose value when used to monitor individual activity. Measurement should focus on improving workflows and alignment at the team level. When metrics are linked to individual monitoring, teams may prioritize visible activity over meaningful progress.
Use collaboration metrics to identify workflow improvements, strengthen coordination, and support better decisions. Team-level insights encourage open participation and maintain trust across functions.
5. Failing to review and adjust metrics
Collaboration evolves as teams scale, adopt new tools, or change workflows. Metrics that remain static over time may lose relevance. Without regular review, teams risk tracking signals that no longer reflect how work actually gets done.
Establish a regular cadence for reviewing collaboration metrics and adjusting them as priorities and workflows change. Continuous refinement ensures that measurement remains aligned with team effectiveness and delivery goals across projects.
Final thoughts
Strong collaboration shapes how consistently teams deliver outcomes, adapt to change, and maintain alignment across complex projects. Measuring collaboration clarifies how work moves, how decisions are made, and where coordination strengthens or slows execution. With the right collaboration metrics in place, teams gain a practical way to improve communication, streamline workflows, and build shared accountability across functions.
Start with a focused set of meaningful metrics, review them consistently, and connect insights to real workflow improvements. When collaboration is measured with intent and used to guide decisions, teams build stronger alignment, improve delivery predictability, and sustain long-term team effectiveness across projects.
Frequently asked questions
Q1. What are collaboration metrics?
Collaboration metrics are measurable indicators that show how effectively teams work together to deliver outcomes. They help organizations evaluate communication quality, decision speed, alignment across teams, and workflow efficiency. Common collaboration metrics include cycle time, lead time, time to decision, dependency resolution time, rework rate, meeting effectiveness, knowledge sharing rate, and team engagement trends.
Q2. What are the key metrics used to measure collaboration?
The most important metrics for measuring team collaboration focus on execution, alignment, and communication. Key collaboration KPIs include:
- Cycle time and lead time
- Time to decision
- Dependency resolution time
- Rework or revision rate
- Project completion predictability
- Response time for critical discussions
- Meeting effectiveness rate
- Documentation and knowledge sharing rate
- Team sentiment and engagement
Tracking these metrics helps organizations understand how collaboration influences delivery speed, quality, and team performance.
Q3. What are the 5 C’s of collaboration?
The 5 C’s of collaboration represent the core elements that support effective teamwork:
- Communication: Clear exchange of information across teams
- Coordination: Alignment of tasks, timelines, and responsibilities
- Cooperation: Willingness to work toward shared goals
- Commitment: Accountability for outcomes and responsibilities
- Contribution: Active participation and knowledge sharing
These five elements help teams maintain alignment, improve coordination, and strengthen team effectiveness across projects.
Q4. What are the 5 P’s of collaboration?
The 5 P’s of collaboration provide a structured framework for building effective teamwork:
- Purpose: Clearly defined shared goals
- People: Defined roles and responsibilities
- Process: Structured workflows and decision-making
- Platforms: Tools that support communication and visibility
- Performance: Measurement of outcomes and effectiveness
This framework helps organizations connect collaboration practices with measurable business and delivery outcomes.
Q5. What are the 4 C’s of collaboration?
The 4 C’s of collaboration describe the foundational capabilities required for effective teamwork:
- Communication: Transparent and consistent information sharing
- Coordination: Alignment across teams and workflows
- Collaboration: Joint problem-solving and shared execution
- Commitment: Accountability toward shared goals
These elements form the foundation for strong collaboration in modern project and product teams.
Recommended for you




