Introduction
A fast-growing product launches new features every quarter and expands into new markets each year. As more teams join the roadmap, more ideas enter discovery, and more stakeholders influence the direction. Growth accelerates opportunity and complexity simultaneously. Scaling product management across teams becomes essential when multiple squads contribute to a single product vision. Clear ownership, aligned goals, and shared planning systems help teams deliver cohesive outcomes. This guide outlines how to scale product teams, structure decision-making, and build a product management system that supports sustainable growth across the organization.
What scaling product management across teams really means
Scaling product management across teams begins long before new roles are added. Most organizations reach a point where multiple teams contribute to a single product or platform, and coordination becomes more difficult than execution. At this stage, scaling product teams requires a structured system that connects strategy, planning, and delivery across every team working on the product.
Scaling product management vs. growing the product team
Many organizations assume scaling product management means hiring more product managers. Headcount growth helps distribute ownership, yet it does not solve alignment or decision clarity. Without shared processes and clear structures, adding more PMs increases coordination overhead and slows decision-making.
Scaling product management focuses on building a system that supports multiple teams working toward shared outcomes. This system includes a clear product strategy, defined ownership areas, consistent prioritization methods, and shared planning cadences. When these elements exist, each team understands its role within the larger product direction.
Common signals that product management needs to scale
Organizations usually experience clear signals before they formally scale product management. These signals appear when coordination across teams becomes harder than building features.
- Roadmaps start diverging across teams: Each team creates its own roadmap based on local priorities. Over time, these roadmaps diverge and create fragmented product experiences. Customers experience inconsistency, and leadership struggles to connect work across teams to the overall strategy.
- Decision bottlenecks slow execution: As product teams grow, more decisions require alignment across functions and leadership. Without defined decision ownership, teams wait for approvals or duplicate discussions. Execution speed drops and delivery timelines stretch.
- Duplicate discovery and delivery work increases: Multiple teams often research the same problems or build similar solutions. Lack of shared discovery insights leads to repeated customer interviews, overlapping features, and inconsistent user experiences. This duplication consumes time that could be used for higher-impact work.
- Leadership lacks visibility across initiatives: Product leaders need visibility into what each team is building, why it matters, and how it connects to company goals. Without a shared system of record, leadership reviews rely on scattered updates and manual reports. This makes prioritization and investment decisions harder.
When these signals appear, scaling product management becomes necessary to maintain clarity and execution speed.
What successful scaling looks like
Successful scaling of product management creates alignment without slowing teams down. Each team operates with autonomy while contributing to shared product goals.
- Consistent product strategy across teams: All teams work toward a unified strategy with clearly defined outcomes. Product initiatives connect directly to company objectives, making prioritization more consistent across teams.
- Autonomous teams with clear ownership: Each product team owns a defined problem space or product area. Ownership boundaries reduce overlap and help teams make decisions quickly within their domain. Clear ownership also improves accountability for outcomes.
- Shared metrics and prioritization frameworks: Teams measure success using consistent definitions and outcome metrics. Shared prioritization frameworks allow leadership to compare initiatives across teams and allocate resources effectively. This consistency strengthens alignment across the product organization.
- Visibility across strategy and execution: Leadership and teams can view product plans, progress, and risks in one place. Shared visibility reduces status meetings and supports faster decision-making. When teams see how their work connects to broader goals, coordination improves naturally.
Scaling product management across teams ultimately creates a system where strategy, ownership, and execution remain connected. Organizations that invest in these foundations build product teams that grow without losing focus or speed.
When teams are ready to scale product management
Scaling product management across teams works best when organizations reach the right level of complexity. Product organizations usually experience operational strain before formally scaling product management. These signals appear when managing multiple product teams becomes harder than delivering outcomes.
Let us now look at the readiness signals that indicate it is time to scale product management, the risks of scaling too early, and how defining a clear scaling goal helps teams move in the right direction.
1. Multiple squads working on the same product
Several teams contribute to one product or platform. Without shared planning and ownership clarity, roadmaps begin to diverge, and priorities become harder to align.
2. Increasing cross-team dependencies
Teams depend on each other for delivery across features, infrastructure, and releases. Coordination effort rises, and delays increase without structured planning.
3. Growing stakeholder complexity
More stakeholders request visibility and input across initiatives. Product teams need clearer communication and prioritization systems to manage expectations.
4. Expansion into multiple product areas
New modules, platforms, or customer segments introduce additional roadmaps and discovery work. Scaling product management becomes necessary to maintain alignment.
Build a clear product strategy and operating model for scale
A structured product operating model helps teams understand what to build, why it matters, and how their work connects to company goals. Let’s explore why aligning strategy becomes more challenging at scale, the key elements of a scalable product operating model, and methods for linking company goals to team-level execution:
Why strategy alignment becomes harder at scale
As organizations scale product teams, decision-making spreads across multiple squads. Each team manages its own roadmap, discovery work, and delivery timelines. Without a shared strategy and clear priorities, teams define success differently and move in separate directions.
Leadership often communicates high-level goals, yet teams need clearer guidance on what those goals mean for their product areas. Consistent strategic direction ensures that scaling product management across teams leads to coordinated outcomes rather than fragmented execution.
Core components of a scalable product operating model
A scalable product operating model provides the structure that connects strategy with execution across teams.
- Vision and strategic priorities: A clearly defined product vision and a small set of strategic priorities guide decision-making across all product teams. These priorities help teams evaluate opportunities and focus on work that supports long-term goals.
- Outcome-driven planning: Focus on measurable outcomes rather than feature output. Shared outcome goals allow teams to align their roadmaps while retaining flexibility in execution.
- Clear ownership boundaries: Each team needs defined ownership across product areas, features, or customer journeys. Clear boundaries reduce overlap and enable faster decisions within each team’s scope.
- Shared rituals and workflows: Common planning cadences, roadmap reviews, and execution workflows create consistency across teams. Shared rituals improve visibility and make coordination easier as the product organization grows.
Connecting company goals to team-level execution
Scaling product management requires aligning company goals with team execution. Product leaders must translate strategic priorities into actionable initiatives, roadmaps, and outcomes. Clear connections between team efforts and company objectives enhance prioritization and alignment. A strong product operating model ensures strategy, planning, and delivery stay unified across teams.
Structure product teams for clarity and ownership at scale
As organizations grow, product complexity increases across features, platforms, and customer segments. A clear structure helps scale product management across teams by defining ownership and reducing coordination gaps. Let us now look at the common product team structures used by growing organizations, how to choose the right structure for your stage, and how team structures evolve as product complexity increases.
Common product team structures
Product organizations use different structures depending on product scope and growth stage. Each structure supports scaling product teams in a different way.
- Centralized structure: A single product leadership group manages strategy and prioritization across teams. This structure works well for smaller organizations or products with limited surface area, where alignment is easier to maintain.
- Embedded product pods: Cross-functional pods own specific features or user journeys. Each pod includes product, engineering, and design roles and operates with high autonomy. This model supports faster execution and clearer ownership across multiple product teams.
- Product area ownership: Teams own defined product areas such as onboarding, analytics, or integrations. Ownership boundaries help teams make independent decisions while maintaining alignment with the overall product strategy.
- Hybrid models: Many organizations adopt a hybrid approach that combines centralized strategy with decentralized execution. Leadership sets direction while individual teams manage discovery and delivery within their areas.
Choosing the right structure for your stage
The ideal product team structure varies by product complexity, company size, and growth stage. Early-stage companies benefit from simple setups for quick decisions, while growing products require clear ownership and cross-functional pods for better coordination. Leaders should ensure the structure promotes collaboration, minimizes dependencies, and enables faster decision-making.
Evolving structure as teams grow
As organizations scale, product team structures evolve with new areas, more squads, and expanded leadership. Regular reviews ensure clarity and alignment amid growing complexity. A structure suited for three teams may not fit ten; continuous evaluation ensures speed, ownership, and strategic alignment as teams grow.
Keep teams autonomous while maintaining product-wide alignment
As product organizations scale, teams need the freedom to move fast within their areas of ownership. Strong alignment systems allow teams to stay autonomous while contributing to shared goals.
Let us now look at why autonomy weakens without alignment, how to define clear decision ownership and guardrails, and which shared planning rituals help keep multiple product teams aligned.
Why autonomy weakens without alignment
Autonomy works when teams understand the broader direction and have visibility into related work across the organization. Without shared goals and visibility, teams prioritize local outcomes that may not align with the overall product strategy.
When multiple product teams operate independently without coordination, roadmaps diverge, and dependencies create delays. Scaling product management across teams requires consistent goals, shared metrics, and visibility into ongoing initiatives so teams can make informed decisions within their scope.
Define decision ownership and guardrails
Clear decision ownership helps teams move quickly while maintaining alignment. Product leaders should define which decisions teams can make independently and which require cross-team or leadership input.
Ownership boundaries should cover roadmap decisions, prioritization changes, and release timelines. Guardrails such as strategic priorities, success metrics, and customer segments guide teams without restricting execution flexibility. This structure helps manage multiple product teams without slowing progress.
Create shared planning and review points
Shared planning and regular reviews align teams without over-coordination. Quarterly planning ties initiatives to company goals, while roadmap reviews clarify upcoming work and dependencies. Cross-team syncs address risks, share updates, and coordinate timelines, fostering alignment while maintaining team autonomy.
Standardize how teams prioritize work across the product
As product organizations grow, each team starts evaluating opportunities using its own criteria. Without a shared prioritization approach, comparing initiatives across teams becomes difficult, and leadership struggles to allocate resources effectively. Standardizing prioritization helps scale product management across teams while keeping decision-making efficient. Let us now look at why prioritization becomes inconsistent at scale:
Why prioritization becomes inconsistent at scale
When managing multiple product teams, each team works closely with its own stakeholders and pursues its own goals. Over time, prioritization decisions begin to reflect local pressures rather than the product-wide strategy. Teams may use different metrics, scoring methods, or assumptions when evaluating work.
This inconsistency creates confusion during planning cycles. Leadership finds it harder to compare initiatives across teams and identify the highest-impact opportunities. Dependencies between teams also become harder to manage when priorities do not align.
Implement a shared prioritization framework
A shared prioritization framework ensures that all product teams evaluate work using common inputs and criteria. This framework should define how teams assess customer impact, business value, effort, and strategic alignment.
Clear evaluation criteria make prioritization discussions more structured and transparent. Decision owners should also be defined so teams understand who finalizes trade-offs when priorities compete. With a shared framework in place, scaling product teams becomes more predictable and aligned with the overall product strategy.
Build a unified feedback and discovery system across teams
As product organizations grow, customer feedback and discovery insights begin to spread across multiple channels. Without a unified system, discovery becomes fragmented, and insights remain underused. Let's dive into the hurdles posed by scattered feedback channels and explore how a unified feedback loop can supercharge product discovery across teams.
The challenge of scattered feedback channels
Customer insights enter the organization through multiple functions.
- Support teams capture issues and feature requests,
- Sales teams gather feedback during conversations,
- and product teams conduct research and usability tests.
When these insights remain in separate systems, teams lack a complete view of customer needs. Product teams often rely on limited data within their own domain. This leads to repeated research, an inconsistent understanding of user problems, and missed opportunities to identify broader patterns. Managing multiple product teams becomes harder when discovery insights remain fragmented.
Create a centralized feedback loop
A centralized feedback loop ensures customer insights are shared across product teams. Inputs from support, sales, analytics, and research should be collected, tagged, and categorized to identify trends. Synthesized feedback informs prioritization, roadmaps, and strategy. A unified system connects insights to decision-making, supporting scalable product teams.
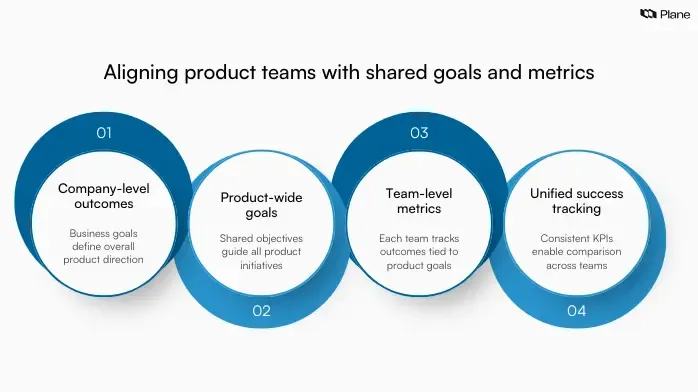
Align all product teams around shared goals and metrics
As product organizations expand, each team starts tracking its own success metrics. Without shared goals and consistent metrics, progress becomes difficult to compare across teams, and leadership loses clarity about the overall impact of the product.
impact of the product
Let's explore how to establish outcome-focused product goals, unify KPI definitions across teams, and apply a north star framework to maintain team alignment:
1. Define outcome-driven product goals
Product goals should align directly with company objectives, such as growth, retention, or engagement. These goals help teams focus on measurable outcomes instead of isolated feature delivery. When product initiatives align with company priorities, teams understand the impact of their work and make better prioritization decisions.
Clear outcome-driven goals also make it easier to evaluate progress across multiple product teams. Leadership can assess which initiatives support strategic direction and adjust investments accordingly.
2. Create consistent KPI definitions across teams
Scaling product teams requires consistent definitions for key performance indicators. Different teams may interpret metrics such as activation, retention, or engagement differently. Inconsistent definitions create confusion and reduce comparability across initiatives.
Standardizing KPI definitions ensures that all teams measure success using the same criteria. Shared dashboards and reporting systems help maintain transparency and improve decision-making across the product organization.
3. Use a north star and supporting metrics
A north star metric provides a shared direction for all product teams. This metric represents the core value delivered to customers and guides long-term product strategy. Supporting metrics help teams measure progress within their specific product areas.
Using a north star framework ensures that multiple product teams move toward the same outcomes while maintaining flexibility in execution. Shared metrics strengthen alignment, improve prioritization, and support effective scaling of product management across teams.
Set up planning and communication cadences that scale
As product teams expand, coordination requires structured planning and communication. Without consistent cadences, teams operate in isolation and leadership struggles to track progress across initiatives. Let us now look at the planning cadences that support scale:
1. Planning cadences that support scale
Consistent planning cycles help product teams align priorities and manage dependencies. Quarterly planning allows leadership and teams to review strategic goals, allocate resources, and define major initiatives. This ensures that all teams move in the same direction.
Sprint planning and short-term execution cycles help teams manage delivery within their product areas. Regular roadmap reviews provide visibility into upcoming work and highlight risks or dependencies across teams. These planning cadences improve coordination across multiple product teams.
2. Communication rhythms across teams
Scaling product teams requires predictable communication across functions and leadership levels. Weekly updates help teams share progress, risks, and key decisions. Cross-team syncs address dependencies and maintain alignment across product areas.
Leadership reviews provide a consolidated view of product progress and help resolve priority conflicts. Clear communication rhythms reduce ad hoc status requests and support faster decision-making across the product organization.
3. Documentation and knowledge sharing
A shared source of truth ensures that strategy, plans, and decisions remain visible across teams. Product documentation should include goals, roadmaps, research insights, and key decisions. Centralized knowledge helps teams access information without relying on manual updates.
Strong documentation practices support scaling product management by improving visibility and reducing confusion. When teams and leadership work from the same information, coordination becomes more efficient and consistent across the organization.
Strengthen the product organization as it grows
Scaling product management across teams requires a strong organizational foundation. As more teams and product areas emerge, hiring, role clarity, and leadership structure directly influence the quality of execution. A well-defined product organization ensures that teams operate with clear expectations and consistent decision standards.
Here's how to build a scalable product organization: hire effectively, establish clear roles and career paths, and preserve product culture as teams grow:
1. Hiring for a scalable product organization
Hiring product managers for a growing organization requires clear role definitions and a structured evaluation process. Each role should align with specific product areas, responsibilities, and expected outcomes. This clarity helps new hires integrate into existing workflows quickly.
Structured interviews focused on problem-solving, prioritization, and stakeholder management ensure consistent hiring decisions. Skill alignment between product, design, and engineering roles also improves collaboration across teams. A systematic hiring approach supports scaling product teams without creating capability gaps.
2. Defining roles and career paths
Clear role definitions help teams understand responsibilities and decision ownership. Product organizations should define expectations for each level, from associate product managers to senior leadership roles. This structure improves accountability and supports professional growth.
Defined career paths also help retain talent and maintain consistency across teams. When product managers understand progression criteria and skill expectations, performance reviews and development planning become more effective.
3. Maintaining product culture at scale
As product organizations expand, maintaining a consistent culture becomes essential. Shared principles guide decision-making and reinforce product values across teams. Decision frameworks help teams evaluate opportunities and resolve tradeoffs consistently.
Collaboration norms such as regular knowledge sharing, cross-team reviews, and transparent communication strengthen alignment. A strong product culture ensures that scaling product management across teams maintains quality, ownership, and focus on customer outcomes.
Wrapping up
Scaling product management across teams requires more than adding new roles or processes. It requires a structured system that connects strategy, ownership, prioritization, and execution across the organization. When teams operate with clear goals, defined ownership, and shared metrics, coordination improves and decisions move faster.
Product organizations that scale successfully invest early in alignment, visibility, and consistent workflows. Clear planning cadences, unified discovery systems, and strong product culture help teams stay focused as complexity grows. With the right structure in place, scaling product management can improve clarity, speed, and product outcomes across every team.
Frequently asked questions
Q1. How do you scale product teams?
Scaling product teams requires clear ownership, shared strategy, and consistent prioritization across teams. Product leaders should define product areas, align teams around common goals, and introduce shared planning cadences and metrics. A unified feedback system and clear decision ownership help multiple product teams move in the same direction while maintaining autonomy.
Q2. What is the 80 20 rule in product management?
The 80 20 rule in product management refers to focusing on the 20 percent of features or improvements that drive 80 percent of customer value or business impact. Product teams use this principle to prioritize high-impact work, reduce unnecessary features, and allocate resources toward initiatives that deliver the strongest outcomes.
Q3. What are the 5 C’s of product management?
The 5 C’s of product management typically include company, customers, competitors, collaborators, and context. These factors help product managers evaluate market opportunities, define product strategy, and make informed prioritization decisions that align with business goals and customer needs.
Q4. What is scalability in product management?
Scalability in product management refers to the ability to manage growing product complexity, team size, and customer demand without sacrificing alignment or execution speed. Scalable product management systems include clear strategy, defined ownership, shared metrics, and consistent workflows that support multiple teams working on a single product or platform.
Q5. What are the 5 P’s of product management?
The 5 P’s of product management commonly include product, price, place, promotion, and people. These elements help product teams define product positioning, go-to-market strategy, and overall product success by aligning product decisions with customer needs and business objectives.
Recommended for you




